LevelDB学习笔记(六) -- LRU缓存
LevelDB学习笔记,本篇学习其LRU缓存实现。
1. 背景
继续学习梳理LevelDB中具体的流程,本篇来看下LRU缓存实现。
说明:本博客作为个人学习实践笔记,可供参考但非系统教程,可能存在错误或遗漏,欢迎指正。若需系统学习,建议参考原链接。
2. LevelDB缓存说明
LevelDB中使用的缓存(cache)主要用于读取场景,使得读取热数据时尽量在缓存中命中,减少读取sstable文件导致的磁盘io。
其使用了一种基于LRUcache(Least Recently Used)的缓存机制,用于缓存:
- 已打开的sstable文件对象和相关元数据;
- sstable中的dataBlock的内容;
LRUcache对应的结构由两部分内容组成:
- Hash table:用来存储数据;
- LRU:用来维护数据项的新旧信息;
其中Hash table是基于Yujie Liu等人的论文《Dynamic-Sized Nonblocking Hash Table》实现的,用来存储数据。论文可见:Dynamic-Sized-Nonblocking-Hash-Tables。
当hash表的数据量增大时,为了保证插入、删除、查找等操作仍保持较为理想的操作效率(O(1)),需要进行resize。基于上述文章实现的hash表可以实现resize过程中不阻塞其他并发请求。
3. 缓存结构
3.1. 缓存类定义:TableCache
在DBImpl中,定义了一个TableCache类指针,这里就是对应的缓存类。
并且在DBImpl类的构造函数中,初始化列表中new了一个缓存类赋值给table_cache_。对应代码为:table_cache_(new TableCache(dbname_, options_, TableCacheSize(options_))),其中第3个参数entries默认990(1000预留10个)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// db/db_impl.h
class DBImpl : public DB {
...
// 此处定义了一个缓存
// table_cache_ provides its own synchronization
TableCache* const table_cache_;
...
// 内存态的表
MemTable* mem_;
// 内存态的表,不可修改
MemTable* imm_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_); // Memtable being compacted
...
}
看下TableCache类的具体定义,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// db/table_cache.h
class TableCache {
public:
TableCache(const std::string& dbname, const Options& options, int entries);
...
Iterator* NewIterator(const ReadOptions& options, uint64_t file_number,
uint64_t file_size, Table** tableptr = nullptr);
// If a seek to internal key "k" in specified file finds an entry,
// call (*handle_result)(arg, found_key, found_value).
Status Get(const ReadOptions& options, uint64_t file_number,
uint64_t file_size, const Slice& k, void* arg,
void (*handle_result)(void*, const Slice&, const Slice&));
// Evict any entry for the specified file number
void Evict(uint64_t file_number);
private:
Status FindTable(uint64_t file_number, uint64_t file_size, Cache::Handle**);
Env* const env_;
const std::string dbname_;
const Options& options_;
// Cache本身是一个抽象类,此处抽象指针用作多态
Cache* cache_;
};
并且在其构造函数中,初始化了Cache* cache_;,通过NewLRUCache创建了对应的实现类实例。
传入的entries即上面的990。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// db/table_cache.cc
// 构造函数,这里cache_初始化为了一个 LRUCache(ShardedLRUCache类)
// DBImpl()构造函数初始化列表中,传进来的entries默认为990
TableCache::TableCache(const std::string& dbname, const Options& options,
int entries)
: env_(options.env),
dbname_(dbname),
options_(options),
cache_(NewLRUCache(entries)) {}
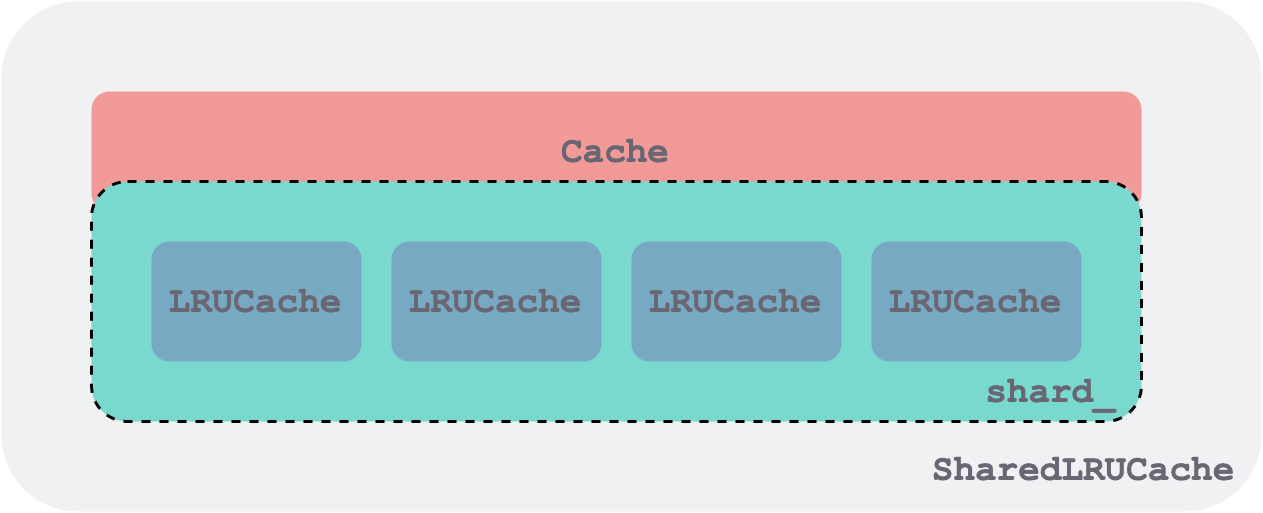
3.2. 缓存实现包装:ShardedLRUCache
1
2
3
// util/cache.cc
// 传入上面的entries(即990)
Cache* NewLRUCache(size_t capacity) { return new ShardedLRUCache(capacity); }
LRU缓存实现类逻辑:实现在LRUCache类,ShardedLRUCache类包含了一个LRUCache类数组,数组成员16个,由key对应的hash进行分片处理。
对应代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
// util/cache.cc
static const int kNumShardBits = 4;
// 即16
static const int kNumShards = 1 << kNumShardBits;
// LRU缓存实现类,包含了 LRUCache 数组
class ShardedLRUCache : public Cache {
private:
// 由一组 LRUCache 组成,每个 LRUCache 作为一个分片,同时是一个加锁的粒度,他们都实现了 Cache 接口
// LRUCache 数组,此处为16个
LRUCache shard_[kNumShards];
port::Mutex id_mutex_;
uint64_t last_id_;
static inline uint32_t HashSlice(const Slice& s) {
return Hash(s.data(), s.size(), 0);
}
static uint32_t Shard(uint32_t hash) { return hash >> (32 - kNumShardBits); }
public:
...
// 插入一个键值对(key,value)到缓存(cache)中
// 返回指向该键值对的句柄(handle),调用者在用完句柄后,需要调用 this->Release(handle) 进行释放
// 在键值对不再被使用时,键值对会被传入的 deleter 参数释放
Handle* Insert(const Slice& key, void* value, size_t charge,
void (*deleter)(const Slice& key, void* value)) override {
// 基于key计算hash
const uint32_t hash = HashSlice(key);
// 选择哪一个 LRUCache分片 来执行Insert操作,具体逻辑在LRUCache中
return shard_[Shard(hash)].Insert(key, hash, value, charge, deleter);
}
// 如果缓存中没有相应键(key),则返回 nullptr;否则返回指向对应键值对的句柄(Handle)。
// 调用者用完句柄后,要记得调用 this->Release(handle) 进行释放
Handle* Lookup(const Slice& key) override {
// 查找也是跟上面一样,key算hash,然后选择某个LRUCache进行处理
const uint32_t hash = HashSlice(key);
return shard_[Shard(hash)].Lookup(key, hash);
}
...
};
3.3. LRU实现逻辑:LRUCache
类定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
// util/cache.cc
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache();
~LRUCache();
// Separate from constructor so caller can easily make an array of LRUCache
void SetCapacity(size_t capacity) { capacity_ = capacity; }
// Like Cache methods, but with an extra "hash" parameter.
Cache::Handle* Insert(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash, void* value,
size_t charge,
void (*deleter)(const Slice& key, void* value));
Cache::Handle* Lookup(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash);
void Release(Cache::Handle* handle);
void Erase(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash);
void Prune();
size_t TotalCharge() const {
MutexLock l(&mutex_);
return usage_;
}
private:
void LRU_Remove(LRUHandle* e);
void LRU_Append(LRUHandle* list, LRUHandle* e);
void Ref(LRUHandle* e);
void Unref(LRUHandle* e);
bool FinishErase(LRUHandle* e) EXCLUSIVE_LOCKS_REQUIRED(mutex_);
// Initialized before use.
size_t capacity_;
// mutex_ protects the following state.
mutable port::Mutex mutex_;
size_t usage_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
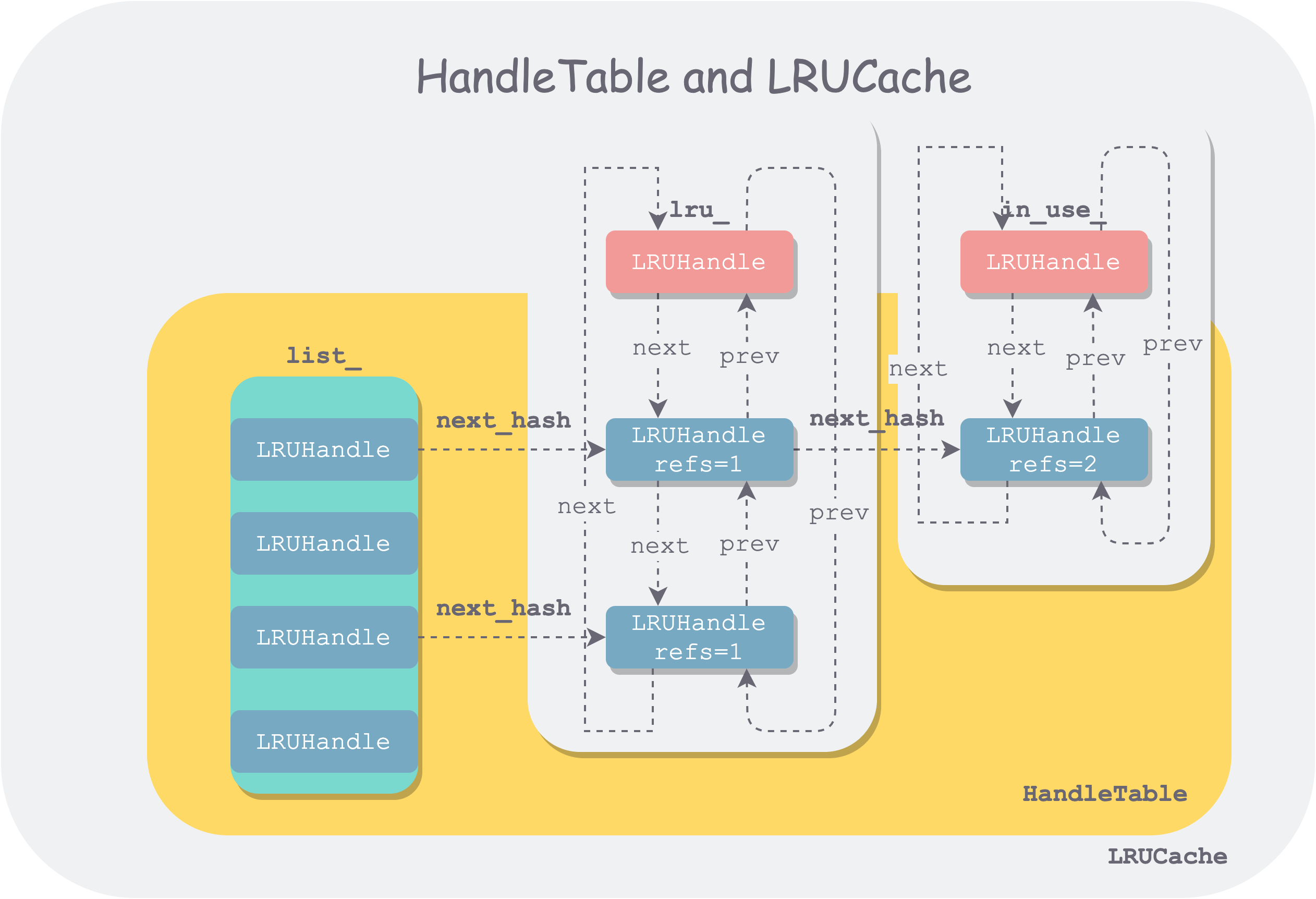
// LevelDB 使用两个双向链表保存数据,缓存中的所有数据要么在一个链表中,要么在另一个链表中,但不可能同时存在于两个链表中。
// 即下面的 lru链表 和 in-use链表
// 哈希表中用来处理冲突的链表节点与双向链表中的节点使用的是同一个数据结构(LRUHandle)
// Dummy head of LRU list.
// lru.prev is newest entry, lru.next is oldest entry.
// Entries have refs==1 and in_cache==true.
// 所有已经不再为客户端使用的条目都放在 lru 链表中,该链表按最近使用时间有序,当容量不够用时,会驱逐此链表中最久没有被使用的条目
// LRUHandle 是双向链表和哈希表的基本构成单位,同时也是数据条目缓存和操作的基本单元。
LRUHandle lru_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
// Dummy head of in-use list.
// Entries are in use by clients, and have refs >= 2 and in_cache==true.
// 所有正在被客户端使用的数据条目(an kv item)都存在该链表中,
// 该链表是无序的,因为在容量不够时,此链表中的条目是一定不能够被驱逐的,因此也并不需要维持一个驱逐顺序。
LRUHandle in_use_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
// 哈希表索引
HandleTable table_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
};
4. 哈希表结构:HandleTable
来看下HandleTable表示的哈希表结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
// util/cache.cc
class HandleTable {
public:
HandleTable() : length_(0), elems_(0), list_(nullptr) { Resize(); }
~HandleTable() { delete[] list_; }
LRUHandle* Lookup(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash) {
return *FindPointer(key, hash);
}
// 哈希表插入节点
LRUHandle* Insert(LRUHandle* h) {
// 找到要插入节点需要的位置
LRUHandle** ptr = FindPointer(h->key(), h->hash);
LRUHandle* old = *ptr;
h->next_hash = (old == nullptr ? nullptr : old->next_hash);
*ptr = h;
if (old == nullptr) {
++elems_;
// 冲突节点超出阈值,需要rehash
if (elems_ > length_) {
// Since each cache entry is fairly large, we aim for a small
// average linked list length (<= 1).
Resize();
}
}
return old;
}
LRUHandle* Remove(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash) {
LRUHandle** ptr = FindPointer(key, hash);
LRUHandle* result = *ptr;
if (result != nullptr) {
*ptr = result->next_hash;
--elems_;
}
return result;
}
private:
// 用于rehash(resize)的判定,rehash后会按*2方式扩大
uint32_t length_;
uint32_t elems_;
LRUHandle** list_;
// 首先使用 hash 值通过位运算,定位到某个桶。然后在该桶中逐个遍历节点
LRUHandle** FindPointer(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash) {
// 根据hash找到slot槽位
LRUHandle** ptr = &list_[hash & (length_ - 1)];
// 遍历同slot下哈希冲突的节点,找一个可插入的位置
while (*ptr != nullptr && ((*ptr)->hash != hash || key != (*ptr)->key())) {
// next_hash也是一个LRUHandle*基本处理单元,这里是hash冲突的节点链表
ptr = &(*ptr)->next_hash;
}
return ptr;
}
void Resize() {
uint32_t new_length = 4;
while (new_length < elems_) {
new_length *= 2;
}
// 创建新hash链表
LRUHandle** new_list = new LRUHandle*[new_length];
memset(new_list, 0, sizeof(new_list[0]) * new_length);
uint32_t count = 0;
// 原来哈希表list_中的记录都hash转移调整到新哈希表
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < length_; i++) {
LRUHandle* h = list_[i];
while (h != nullptr) {
LRUHandle* next = h->next_hash;
uint32_t hash = h->hash;
LRUHandle** ptr = &new_list[hash & (new_length - 1)];
h->next_hash = *ptr;
*ptr = h;
h = next;
count++;
}
}
assert(elems_ == count);
// 释放原来的哈希表空间
delete[] list_;
// 指向扩容后的新哈希表
list_ = new_list;
length_ = new_length;
}
};
4.1. 节点插入流程
从LRUCache::Insert入口,会向哈希表新增记录。
这里会体现:LevelDB 使用两个双向链表保存数据,缓存中的所有数据要么在一个链表中,要么在另一个链表中,但不可能同时存在于两个链表中,即 lru链表 和 in-use链表。
并涉及哈希表的rehash判断。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
// util/cache.cc
Cache::Handle* LRUCache::Insert(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash, void* value,
size_t charge,
void (*deleter)(const Slice& key,
void* value)) {
MutexLock l(&mutex_);
// 创建一个 LRUHandle 基本处理单元
LRUHandle* e =
reinterpret_cast<LRUHandle*>(malloc(sizeof(LRUHandle) - 1 + key.size()));
e->value = value;
e->deleter = deleter;
e->charge = charge;
e->key_length = key.size();
e->hash = hash;
e->in_cache = false;
// 传入引用也算一个计数,后面若在LRU缓存则再+1(即2)
e->refs = 1; // for the returned handle.
std::memcpy(e->key_data, key.data(), key.size());
if (capacity_ > 0) {
e->refs++; // for the cache's reference.
e->in_cache = true;
// 加到 in-use 对应的LRU缓存里,加到in_use_链表头部
LRU_Append(&in_use_, e);
usage_ += charge;
// 新节点加到哈希表里去:`table_.Insert(e)`;
// 并将当前节点从 _lru 缓存里移除(为便于区分,统一按in-use和_lru的说法来区分两个缓存链表)
// 移除操作只是先修改前后节点指向,从链表里断开该节点,不做空间释放
FinishErase(table_.Insert(e));
} else { // don't cache. (capacity_==0 is supported and turns off caching.)
// next is read by key() in an assert, so it must be initialized
e->next = nullptr;
}
// 使用量超出缓存总量,做LRU清理操作
while (usage_ > capacity_ && lru_.next != &lru_) {
LRUHandle* old = lru_.next;
assert(old->refs == 1);
bool erased = FinishErase(table_.Remove(old->key(), old->hash));
if (!erased) { // to avoid unused variable when compiled NDEBUG
assert(erased);
}
}
return reinterpret_cast<Cache::Handle*>(e);
}
哈希表操作,如table_.Insert(e)、table_.Remove,见上面的HandleTable类说明。
其中的LRU_Append逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
void LRUCache::LRU_Append(LRUHandle* list, LRUHandle* e) {
// Make "e" newest entry by inserting just before *list
// 链表操作,要新增的节点e,插入到list节点前面
e->next = list;
e->prev = list->prev;
// 前驱后继节点均调整对应指向
e->prev->next = e;
e->next->prev = e;
}
5. 小结
学习梳理LRU缓存实现逻辑。目前跟踪梳理代码并结合参考链接学习,没有系统进行整理,进一步整理和画图后续再考虑。
6. 参考
1、leveldb