ioserver服务实验(二) -- epoll使用梳理
基于ioserver demo项目,梳理epoll的使用。
基于ioserver demo项目,梳理epoll的使用。
1. 背景
基于C++实现的读写服务demo,借此作为场景温习并深入学习io多路复用、性能调试、MySQL/Redis等开源组件。
本篇先看理论,后续再进行运行调试。梳理demo里面的几个io多路复用实现,并比较 muduo网络库 中的epoll使用进行学习,而后了解内核中的的epoll实现。
参考:
结合之前 TCP半连接全连接(一) – 全连接队列相关过程 里梳理走读的内核相关结构定义和流程,加深印象和理解。
2. epoll一般使用流程
epoll api的一般使用流程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
// 1、使用epoll_create1创建 epoll 实例
int epoll_fd = epoll_create1(0);
// 2、添加监控文件描述符到 epoll 实例。假设已有 listenfd 进行了监听
struct epoll_event event;
// 指定监听读事件
event.events = EPOLLIN;
event.data.fd = listenfd;
epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &event);
// 3、等待事件发生
struct epoll_event events[10]; // 用于存储发生事件的文件描述符信息,此处最大监听10个事件
int num_events = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, events, 10, 1000); // 等待epoll实例上的事件发生,最多等待1000毫秒(1秒)
// 返回值num_events表示发生了多少个事件,events数组会存储这些事件信息
if (num_events == -1) {
// 出现错误
} else if (num_events == 0) {
// 超时时间内没有事件发生
} else {
// 有事件发生,遍历events数组处理事件
for (int i = 0; i < num_events; i++) {
int fd = events[i].data.fd;
if (fd == listenfd) {
// accept处理新的连接请求
// 然后通过epoll_ctl把新的连接文件描述符fd也添加到epoll实例中,进行 EPOLLIN 监听
} else {
if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
// 读事件发生,进行read和业务处理
}
// 关闭之前添加到epoll中的文件描述符fd
close(fd);
}
}
}
// 4、使用完epoll实例后,关闭之前添加到epoll中的文件描述符fd 和 epoll实例
// 关闭之前添加到epoll中的文件描述符
close(listenfd);
// 关闭epoll实例
close(epoll_fd);
3. demo中epoll使用流程走读
项目代码:ioserver_demo
来看下demo里的实现,作为基准以便和优秀的开源项目对比,识别坏味道和值得借鉴学习的部分。
3.1. 抽象类定义
1、抽象类定义,还是比较清晰的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
// include/io_multiplexing.h
// IO多路复用接口抽象类
class IOMultiplexing {
public:
virtual ~IOMultiplexing() = default;
// 添加监听事件
virtual bool addEvent(int fd, EventType type) = 0;
// 移除监听事件
virtual bool removeEvent(int fd, EventType type) = 0;
// 修改监听事件
virtual bool modifyEvent(int fd, EventType type) = 0;
// 等待事件发生
virtual int wait(std::vector<Event>& events, int timeout = -1) = 0;
};
// Epoll实现
class EpollIO : public IOMultiplexing {
private:
int epollfd_;
std::vector<epoll_event> events_;
public:
EpollIO(int max_events = 1024);
~EpollIO() override;
bool addEvent(int fd, EventType type) override;
bool removeEvent(int fd, EventType type) override;
bool modifyEvent(int fd, EventType type) override;
int wait(std::vector<Event>& events, int timeout = -1) override;
};
构造时就用epoll_create1创建了epoll句柄,并初始化了vector容量:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// include/io_multiplexing.cpp
EpollIO::EpollIO(int max_events) : events_(max_events) {
epollfd_ = epoll_create1(0);
if (epollfd_ < 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("epoll_create1 failed");
}
}
3.2. epoll api封装
1、基本socket api创建socket并监听,实例化EpollIO类:io_ = std::make_unique<io::EpollIO>();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
// src/server/server.cpp
class Server {
bool init(const std::string& config_path) {
...
// 创建服务器socket
serverfd_ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (serverfd_ < 0) {xxx}
// 设置socket选项
int opt = 1;
if (setsockopt(serverfd_, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt)) < 0) {xxx}
// 绑定地址
struct sockaddr_in addr{};
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
addr.sin_port = htons(port_);
if (bind(serverfd_, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr)) < 0) {xxx}
// 监听连接
if (listen(serverfd_, SOMAXCONN) < 0) {xxx}
// 设置为非阻塞模式
if (!setNonBlocking(serverfd_)) {xxx}
...
// 创建IO多路复用对象
io_ = std::make_unique<io::EpollIO>();
// 添加 listen fd 到监控列表
io_->addEvent(serverfd_, io::EventType::READ);
...
}
...
};
上述addEvent中封装了epoll_ctl接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// src/server/io_multiplexing.cpp
bool EpollIO::addEvent(int fd, EventType type) {
if (fd < 0) return false;
epoll_event ev{};
ev.data.fd = fd;
// 传入时可以指定多个事件,如 EventType::READ | EventType::WRITE
if (static_cast<int>(type) & static_cast<int>(EventType::READ))
ev.events |= EPOLLIN;
if (static_cast<int>(type) & static_cast<int>(EventType::WRITE))
ev.events |= EPOLLOUT;
if (static_cast<int>(type) & static_cast<int>(EventType::ERROR))
ev.events |= EPOLLERR;
return epoll_ctl(epollfd_, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &ev) == 0;
}
2、主循环中,int nfds = io_->wait(events, 1000);进行epoll_wait等待
1)如果是监听句柄,则调用handleNewConnection处理新连接。
- 其中会
accept接收新连接 -> 设置非阻塞 -> 调用io_->addEvent将新连接句柄加入监控列表
2)如果是客户端句柄,则将请求加入线程池处理。此处捕获当前对象指针并传入客户端fd
handleClient处理中,进行recv接收数据、解析json、Redis和MySQL操作,并发送响应、关闭连接- 此处:客户端句柄的
close关闭和是否epoll_ctl移除,还需要进一步考虑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
class Server {
void run() {
logger_->info("Server started on port " + std::to_string(port_));
// 主事件循环
while (running) {
std::vector<io::Event> events;
int nfds = io_->wait(events, 1000); // 1秒超时
if (nfds < 0) {
if (errno == EINTR) continue;
logger_->error("IO wait error");
break;
}
for (const auto& event : events) {
if (event.fd == serverfd_) {
handleNewConnection();
} else {
// 将客户端请求加入线程池
threadPool_.enqueue([this, fd = event.fd] {
handleClient(fd);
});
}
}
}
cleanup();
}
}
io_->wait中对应的epoll override实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// src/server/io_multiplexing.cpp
int EpollIO::wait(std::vector<Event>& events, int timeout) {
int ret = epoll_wait(epollfd_, events_.data(), events_.size(), timeout);
if (ret < 0) return -1;
events.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < ret; ++i) {
// 初始化暂时用读事件,下面根据实际调整,如果仅是写事件触发,不会多出读?
Event event{events_[i].data.fd, EventType::READ, nullptr};
if (events_[i].events & EPOLLIN)
event.type = EventType::READ;
else if (events_[i].events & EPOLLOUT)
event.type = EventType::WRITE;
else if (events_[i].events & EPOLLERR)
event.type = EventType::ERROR;
events.push_back(event);
}
return ret;
}
4. muduo网络库中的epoll
4.1. 抽象类定义
1、抽象类定义为class Poller,并通过静态函数Poller::newDefaultPoller返回具体的实例,环境变量里没指定MUDUO_USE_POLL则默认epoll。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
// muduo/net/Poller.h
class Poller : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
typedef std::vector<Channel*> ChannelList;
Poller(EventLoop* loop);
virtual ~Poller();
/// Polls the I/O events.
/// Must be called in the loop thread.
virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels) = 0;
/// Changes the interested I/O events.
/// Must be called in the loop thread.
virtual void updateChannel(Channel* channel) = 0;
/// Remove the channel, when it destructs.
/// Must be called in the loop thread.
virtual void removeChannel(Channel* channel) = 0;
virtual bool hasChannel(Channel* channel) const;
static Poller* newDefaultPoller(EventLoop* loop);
void assertInLoopThread() const
{
ownerLoop_->assertInLoopThread();
}
protected:
typedef std::map<int, Channel*> ChannelMap;
// 此处是加到监控中的句柄 和 其对应数据,组成的一个map
// 对于epoll,对应的是epoll_event结构中的data.ptr信息
ChannelMap channels_;
private:
EventLoop* ownerLoop_;
};
// muduo/net/poller/DefaultPoller.cc
Poller* Poller::newDefaultPoller(EventLoop* loop)
{
if (::getenv("MUDUO_USE_POLL"))
{
return new PollPoller(loop);
}
else
{
return new EPollPoller(loop);
}
}
2、实现封装了poll(PollPoller类)和epoll(EPollPoller类)两种io复用机制,此处仅看epoll
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// muduo/net/poller/EPollPoller.h
class EPollPoller : public Poller
{
public:
EPollPoller(EventLoop* loop);
virtual ~EPollPoller();
// 其中进行 ::epoll_wait 等待
virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels);
virtual void updateChannel(Channel* channel);
virtual void removeChannel(Channel* channel);
private:
static const int kInitEventListSize = 16;
static const char* operationToString(int op);
void fillActiveChannels(int numEvents,
ChannelList* activeChannels) const;
void update(int operation, Channel* channel);
typedef std::vector<struct epoll_event> EventList;
// epoll实例句柄
int epollfd_;
EventList events_;
};
4.2. epoll api封装
1、EPollPoller::poll中封装了epoll_wait接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
Timestamp EPollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels)
{
// 当前有哪些监控句柄
LOG_TRACE << "fd total count " << channels_.size();
int numEvents = ::epoll_wait(epollfd_,
&*events_.begin(),
static_cast<int>(events_.size()),
timeoutMs);
int savedErrno = errno;
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());
if (numEvents > 0)
{
LOG_TRACE << numEvents << " events happended";
// 有事件发生,并填充到 activeChannels 里对外提供
fillActiveChannels(numEvents, activeChannels);
// 由于events_对应的vector初始化容量为16(kInitEventListSize),此处考虑扩容
// 相比于demo里直接默认1024,此处细节值得学习
if (implicit_cast<size_t>(numEvents) == events_.size())
{
events_.resize(events_.size()*2);
}
}
else if (numEvents == 0)
{
LOG_TRACE << "nothing happended";
}
else
{
// error happens, log uncommon ones
if (savedErrno != EINTR)
{
errno = savedErrno;
LOG_SYSERR << "EPollPoller::poll()";
}
}
return now;
}
2、epoll_ctl则在EPollPoller::updateChannel和EPollPoller::removeChannel中使用
具体用法,需要结合使用EPollPoller类的demo来跟踪。
从muduo仓库的examples中找个简单的例子:examples/pingpong。
4.3. ping-pong demo
查看examples/pingpong的代码(完整代码见:github),使用TcpServer作为服务端,其中Poller、EPollPoller负责EventLoop事件循环类中的轮询处理。
下面是pingpong demo的服务端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
// examples/pingpong/server.cc
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc < 4)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: server <address> <port> <threads>\n");
}
else
{
LOG_INFO << "pid = " << getpid() << ", tid = " << CurrentThread::tid();
Logger::setLogLevel(Logger::WARN);
const char* ip = argv[1];
uint16_t port = static_cast<uint16_t>(atoi(argv[2]));
InetAddress listenAddr(ip, port);
int threadCount = atoi(argv[3]);
EventLoop loop;
TcpServer server(&loop, listenAddr, "PingPong");
server.setConnectionCallback(onConnection);
server.setMessageCallback(onMessage);
if (threadCount > 1)
{
server.setThreadNum(threadCount);
}
server.start();
loop.loop();
}
}
void onMessage(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn, Buffer* buf, Timestamp)
{
conn->send(buf);
}
有挺大一部分逻辑是在tcp服务端、线程池的处理上,内容挺多,梳理学习了一下其中的逻辑,此处不做展开,几个关键类:
TcpServerTCP服务端抽象,实现中需要涉及下述功能类Acceptor负责监听和accept,作为TcpServer类的一个成员acceptor_- 重点关注向
acceptor_设置的回调函数:TcpServer::newConnection,负责在有新的客户端连接时的处理 Socket包装
EventLoop事件循环,epoll负责事件的轮询通知Channel状态流转处理
EventLoopThreadPool线程池- 单个线程类是
EventLoopThread - 除了实例化TcpServer时的
EventLoop,在每个线程类中还各有一个EventLoop实例
- 单个线程类是
Channel作为自定义数据传给epoll_event的指针,其中包含epoll控制的很多信息- fd、监控的事件类型、有什么类型的事件发生、回调处理函数、事件信息打印之类的辅助类
demo启动流程:server.start() -> loop_->runInLoop -> 调用到Acceptor::listen -> acceptChannel_.enableReading();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// muduo/net/Channel.h
void enableReading() { events_ |= kReadEvent; update(); }
// muduo/net/Channel.cc
const int Channel::kNoneEvent = 0;
const int Channel::kReadEvent = POLLIN | POLLPRI;
const int Channel::kWriteEvent = POLLOUT;
上面update()对应Channel::update() -> 接着调用EventLoop::updateChannel -> poller_->updateChannel(channel) -> EPollPoller::update,里面负责关注句柄事件的状态流转和控制
1
2
3
4
5
6
// muduo/net/Channel.cc
void Channel::update()
{
addedToLoop_ = true;
loop_->updateChannel(this);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// muduo/net/EventLoop.cc
void EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel* channel)
{
assert(channel->ownerLoop() == this);
assertInLoopThread();
poller_->updateChannel(channel);
}
有新连接建立时,设置相应的处理回调,并会调用TcpConnection::connectEstablished,其中还是关注读事件:channel_->enableReading();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
// muduo/net/TcpServer.cc
void TcpServer::newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
EventLoop* ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop();
char buf[64];
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "-%s#%d", ipPort_.c_str(), nextConnId_);
++nextConnId_;
string connName = name_ + buf;
LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::newConnection [" << name_
<< "] - new connection [" << connName
<< "] from " << peerAddr.toIpPort();
InetAddress localAddr(sockets::getLocalAddr(sockfd));
// FIXME poll with zero timeout to double confirm the new connection
// FIXME use make_shared if necessary
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop,
connName,
sockfd,
localAddr,
peerAddr));
connections_[connName] = conn;
conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);
conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);
conn->setWriteCompleteCallback(writeCompleteCallback_);
conn->setCloseCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, _1)); // FIXME: unsafe
ioLoop->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn));
}
4.4. 用法小结
通过上面梳理学习ping-pong demo的流程,可看到epoll的关注事件变化:
- 服务监听时,注册读事件,
POLLIN | POLLPRI(poll和epoll的事件类型定义的值相同) - accept到新连接请求,注册读事件
- 向客户端发送数据没发完时,注册写事件,
POLLOUT- 调用链比较长,起始于main函数设置回调:
onMessage->conn->send(buf)->TcpConnection::send(Buffer* buf)->TcpConnection::sendInLoop(const void* data, size_t len)->channel_->enableWriting();
- 连接关闭时,
- 先执行
TcpServer::removeConnection - 而后是回调处理:
TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop TcpConnection::connectDestroyed->channel_->disableAll();- 其实现为:
void disableAll() { events_ = kNoneEvent; update(); } kNoneEvent状态即没有关注任何事件类型,会在EPollPoller::updateChannel中将该类型EPOLL_CTL_DEL处理
- 先执行
- 均基于默认的
水平触发模式,若有数据则会一直触发
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
// muduo/net/poller/EPollPoller.cc
void EPollPoller::updateChannel(Channel* channel)
{
if (index == kNew || index == kDeleted)
{
...
}
else
{
...
assert(index == kAdded);
// 此处处理 kNoneEvent 状态的句柄
if (channel->isNoneEvent())
{
// 其中使用 epoll_ctl 将句柄从epoll中移除
update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL, channel);
channel->set_index(kDeleted);
}
else
{
update(EPOLL_CTL_MOD, channel);
}
}
}
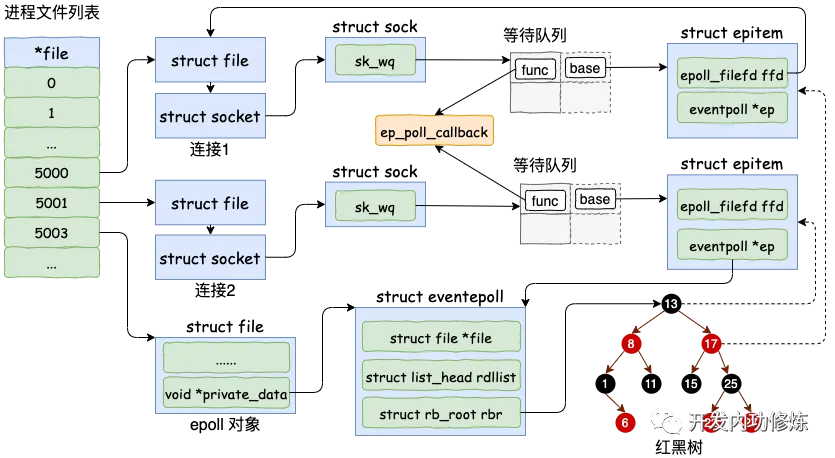
5. 内核中的epoll实现
先简单过了一下参考链接中的流程:深入揭秘 epoll 是如何实现 IO 多路复用的
5.10内核中epoll的实现,后续再跟踪,此处只简单看一下epoll的实例创建,其中eventpoll里的struct rb_root_cached rbr结构是红黑树:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
// linux-5.10.10/fs/eventpoll.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create1, int, flags)
{
return do_epoll_create(flags);
}
static int do_epoll_create(int flags)
{
int error, fd;
struct eventpoll *ep = NULL;
struct file *file;
...
// 创建内部数据结构:`struct eventpoll`
error = ep_alloc(&ep);
if (error < 0)
return error;
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (fd < 0) {
error = fd;
goto out_free_ep;
}
file = anon_inode_getfile("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep,
O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
...
ep->file = file;
fd_install(fd, file);
return fd;
...
out_free_ep:
ep_free(ep);
return error;
}
// linux-5.10.10/fs/eventpoll.c
// 其中`struct rb_root_cached rbr`是红黑树
struct eventpoll {
struct mutex mtx;
/* Wait queue used by sys_epoll_wait() */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
/* Wait queue used by file->poll() */
wait_queue_head_t poll_wait;
/* List of ready file descriptors */
struct list_head rdllist;
/* Lock which protects rdllist and ovflist */
rwlock_t lock;
/* RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs */
struct rb_root_cached rbr;
...
};
可以看到struct file和struct eventpoll之间有关联关系,贴一下参考链接的内核数据结构图,比较直观:
图中是基于3.10内核,结构体定义有所差别,不过整体流程一致,此处可作为参考。
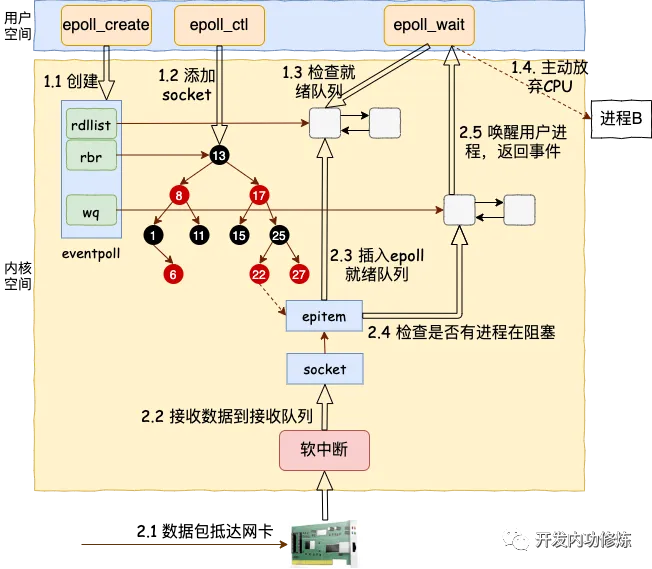
epoll工作流程示意图:
6. 小结
梳理了demo和muduo库中的epoll使用,顺便学习了一下muduo库的整体流程。简单基于参考链接看了下epoll在内核中的基本流程,后续再深入学习。
对比muduo库里的epoll使用,ioserver demo里用法还比较粗糙,后续调整为集成muduo库进行实验,另一方面,数据库操作等也需逐步改造优化。