梳理Redis中的epoll机制
梳理 Redis 中的epoll机制。
梳理 Redis 和 Nginx 中的epoll机制。
1. 背景
前面的ioserver demo中进行了基本的epoll机制使用,并梳理了开源网络库 muduo 的epoll使用和线程池实现。
本篇继续epoll在Redis和Nginx中的使用,进一步加深理解。跟踪的源码分支保持和本地CentOS8环境安装的服务版本一致:Redis版本:5.0.3(单线程版本)、Nginx版本:1.14。
参考:
- 深度解析单线程的 Redis 如何做到每秒数万 QPS 的超高处理能力!
- 说明:redis 6.0后支持了多线程,可参考学习:Redis 6 中的多线程是如何实现的!?
- 万字多图,搞懂 Nginx 高性能网络工作原理!
- Redis 5.0.3 源码
- Nginx 1.14 源码
2. Redis中的epoll流程
2.1. Redis服务入口
整个Redis的服务入口在:src/server.c,通过理解其中epoll的工作流程,有助于梳理Redis整体功能和代码。简化如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// redis-5.0.3/src/server.c
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
...
// 启动初始化
initServer();
...
// 运行事件处理循环,一直到服务器关闭为止
// 其中server是全局类,定义:`struct redisServer server;`
aeMain(server.el);
...
}
initServer()逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// redis-5.0.3/src/server.c
void initServer(void) {
...
// 1、创建事件循环 (`struct aeEventLoop`结构)
server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+CONFIG_FDSET_INCR);
...
// 2、监听端口
if (server.port != 0 &&
listenToPort(server.port,server.ipfd,&server.ipfd_count) == C_ERR)
exit(1);
...
// 3、注册 accept事件处理器 到epoll事件循环中
for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR)
{
serverPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
}
}
...
}
aeMain(server.el)对应函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// redis-5.0.3/src/ae.c
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
// 事件处理
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);
}
}
2.2. epoll初始化创建
来看一下上面void initServer(void) 中 aeCreateEventLoop 的实现流程。
先看下核心数据结构:aeEventLoop,里面封装了具体io多路复用事件机制,事件机制对应的结构在 void *apidata; 中。
Redis事件机制代码里很多字段或者文件名都有 ae、ae_ 前缀,从下面代码块中的注释:A simple event-driven programming library 可以看出ae就是指“一个事件驱动库(an event-driven library)”。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// redis-5.0.3/src/ae.h
/* A simple event-driven programming library. Originally I wrote this code
* for the Jim's event-loop (Jim is a Tcl interpreter) but later translated
* it in form of a library for easy reuse.
* xxxxx
*/
typedef struct aeEventLoop {
int maxfd; /* highest file descriptor currently registered */
int setsize; /* max number of file descriptors tracked */
long long timeEventNextId;
time_t lastTime; /* Used to detect system clock skew */
aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events */
aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events */
aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead;
int stop;
// 指向具体io多路复用机制的数据结构,如 使用epoll时,使用的aeApiState结构里就包含epoll_event
void *apidata; /* This is used for polling API specific data */
aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep;
aeBeforeSleepProc *aftersleep;
} aeEventLoop;
aeCreateEventLoop函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// redis-5.0.3/src/ae.c
aeEventLoop *aeCreateEventLoop(int setsize) {
aeEventLoop *eventLoop;
int i;
// 申请空间创建 aeEventLoop
if ((eventLoop = zmalloc(sizeof(*eventLoop))) == NULL) goto err;
eventLoop->events = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFileEvent)*setsize);
eventLoop->fired = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFiredEvent)*setsize);
if (eventLoop->events == NULL || eventLoop->fired == NULL) goto err;
eventLoop->setsize = setsize;
...
eventLoop->aftersleep = NULL;
// 创建具体io多路复用机制用到的数据结构
// 根据上面的 #ifdef 条件编译判断,选择对应的实现,比如:HAVE_EVPORT、HAVE_EPOLL、HAVE_KQUEUE,对应不同的操作系统
if (aeApiCreate(eventLoop) == -1) goto err;
...
}
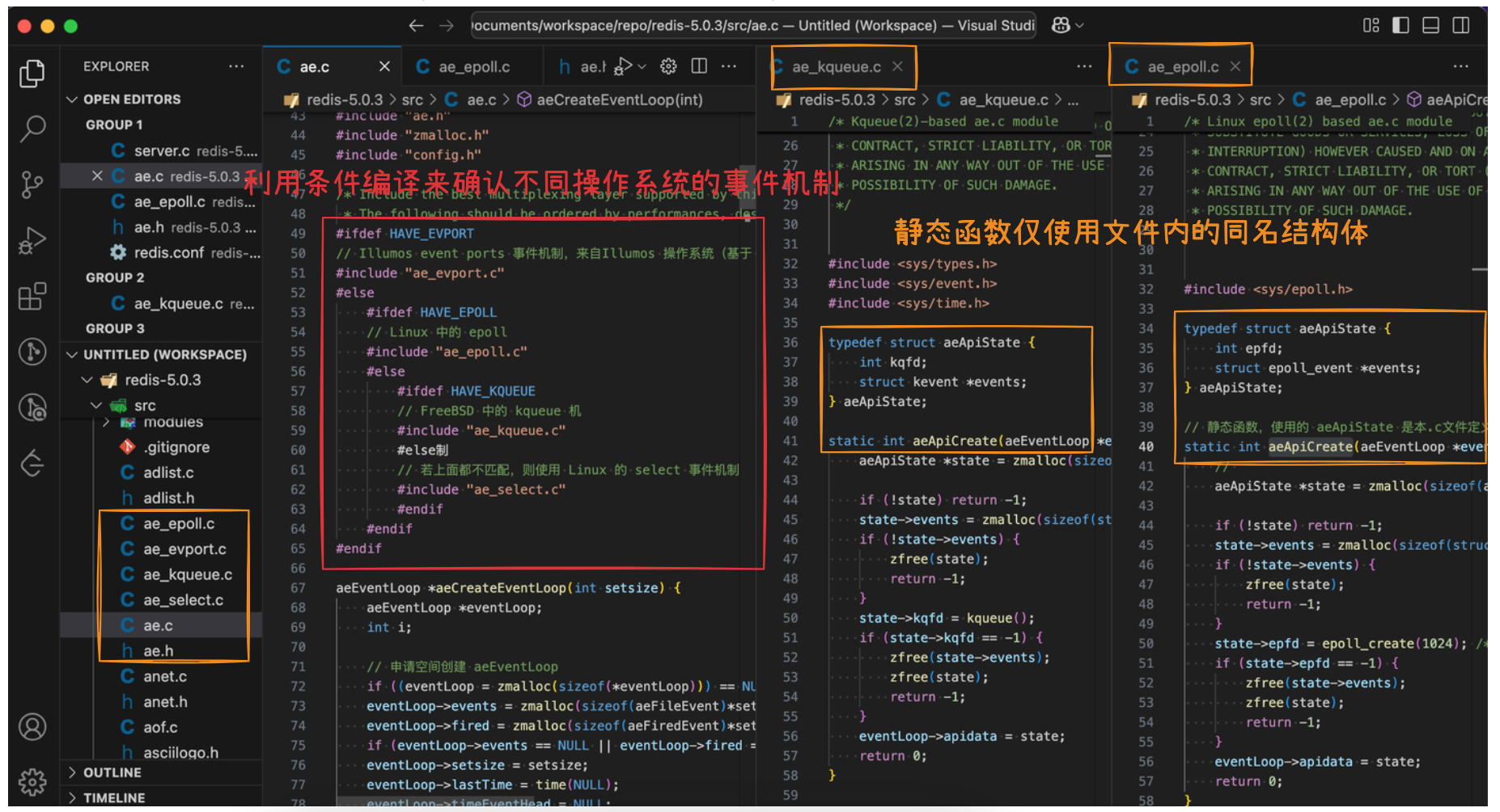
代码中,基于条件编译来确认不同操作系统上的io多路复用机制,各机制实现里都包含aeApiCreate接口和对应的数据结构,其中:
ae_evport.c使用Illumos event ports事件机制,来自Illumos操作系统(基于 OpenSolaris 的开源操作系统)ae_epoll.c使用epoll事件机制,来自Linux操作系统ae_kqueue.c使用kqueue事件机制,来自BSD操作系统ae_select.c使用select事件机制,来自Unix操作系统,上面那些机制都没有则使用select机制
如下图所示:
本篇文章里只关注epoll,所以查看ae_epoll.c,里面使用了epoll_create创建epoll句柄
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// redis-5.0.3/src/ae_epoll.c
typedef struct aeApiState {
int epfd;
struct epoll_event *events;
} aeApiState;
// 静态函数,使用的 aeApiState 是本.c文件定义的,对应epoll的数据结构(其他c文件里也有同名的 aeApiState 结构)
static int aeApiCreate(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
aeApiState *state = zmalloc(sizeof(aeApiState));
if (!state) return -1;
state->events = zmalloc(sizeof(struct epoll_event)*eventLoop->setsize);
if (!state->events) {
zfree(state);
return -1;
}
state->epfd = epoll_create(1024); /* 1024 is just a hint for the kernel */
if (state->epfd == -1) {
zfree(state->events);
zfree(state);
return -1;
}
eventLoop->apidata = state;
return 0;
}
2.3. 服务监听
即上面initServer(void)中的listenToPort(server.port,server.ipfd,&server.ipfd_count)。
Redis中支持绑定多个网络地址,所以下面监听是一个循环,兼容ipv6。监听后,设置监听fd为非阻塞。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
// redis-5.0.3/src/server.c
int listenToPort(int port, int *fds, int *count) {
for (j = 0; j < server.bindaddr_count || j == 0; j++) {
// 若为NULL,则ipv4和ipv6都监听
if (server.bindaddr[j] == NULL) {
// tcp_backlog 指定tcp全连接队列最大长度
// 里面设置SO_REUSEADDR,并开启监听 bind再listen
fds[*count] = anetTcp6Server(server.neterr,port,NULL, server.tcp_backlog);
...
fds[*count] = anetTcpServer(server.neterr,port,NULL,
} else if (strchr(server.bindaddr[j],':')) {
// ipv6形式的地址示例:2001:db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334,还涉及简化写法
/* Bind IPv6 address. */
fds[*count] = anetTcp6Server(server.neterr,port,server.bindaddr[j], server.tcp_backlog);
} else {
/* Bind IPv4 address. */
fds[*count] = anetTcpServer(server.neterr,port,server.bindaddr[j], server.tcp_backlog);
}
...
// 所有监听fd设置非阻塞 O_NONBLOCK:fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags)
anetNonBlock(NULL,fds[*count]);
...
}
}
可看到全连接队列(ss中listening状态的句柄) Send-Q只有128,而redis.conf中默认配置的tcp-backlog为511。这是因为系统listen时取min(传入的backlog, 系统net.core.somaxconn)。
TCP全连接队列和ss/netstat相关分析,可以参考之前的学习实践笔记:TCP半连接全连接(一) – 全连接队列相关过程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[CentOS-root@xdlinux ➜ ~ ]$ netstat -anpt|grep -E "redis|Send-Q"
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 86222/redis-server
[CentOS-root@xdlinux ➜ ~ ]$ ss -anpt|grep -E "redis|Send-Q"
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6379 0.0.0.0:* users:(("redis-server",pid=86222,fd=6))
# net.core.somaxconn 参数是128
[CentOS-root@xdlinux ➜ ~ ]$ sysctl net.core.somaxconn
net.core.somaxconn = 128
2.4. 事件注册
继续看initServer(void):
监听端口的读事件,注册处理函数为:acceptTcpHandler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// redis-5.0.3/src/server.c
// 3、注册 accept事件处理器 到epoll事件循环中
for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR)
{
serverPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// redis-5.0.3/src/ae.c
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask,
aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData)
{
...
// aeEventLoop结构中的 aeFileEvent *events,对应的 aeFileEvent 结构包含了回调函数和自定义数据
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];
...
// 按实际的事件处理器分别处理,epoll 对应 ae_epoll.c
// 其中使用 epoll_ctl 注册事件,事件类型由 mask 指定
if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1)
return AE_ERR;
fe->mask |= mask;
// 根据传入的事件类型,设置对应的回调函数,设置到`aeFileEvent`结构中
if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc;
fe->clientData = clientData;
...
}
aeFileEvent结构定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// redis-5.0.3/src/ae.h
typedef struct aeFileEvent {
int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE|BARRIER) */
aeFileProc *rfileProc; // 读事件回调
aeFileProc *wfileProc; // 写事件回调
void *clientData; // 一些额外扩展数据
} aeFileEvent;
2.5. 事件循环处理
上述initServer()里进行完事件循环初始化创建、服务监听、事件注册后,aeMain中进行事件循环处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// redis-5.0.3/src/server.c
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
...
initServer();
...
aeMain(server.el);
...
}
// redis-5.0.3/src/ae.c
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
// 如果有需要在事件处理前执行的函数,则执行
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
// 循环处理所有事件(包含fd和定时器)
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);
}
}
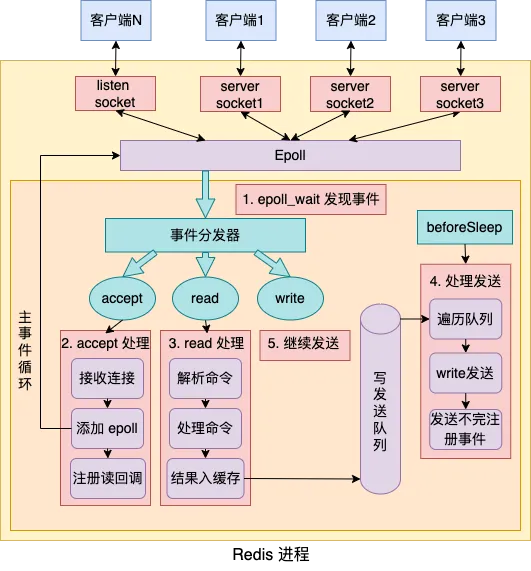
主要看 aeProcessEvents 的事件处理流程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// redis-5.0.3/src/ae.c
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
...
// 其中进行 epoll_wait
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
// 事件信息
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
...
// 读事件,回调处理
if (!invert && fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
fired++;
}
// 写事件,回调处理
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc) {
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
fired++;
}
}
...
processed++;
}
...
}
前面initServer里初始化时,读事件回调注册为了acceptTcpHandler,看下具体处理流程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// redis-5.0.3/src/networking.c
void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
...
while(max--) {
// 里面循环accept,接收到就break并返回客户端fd
cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);
if (cfd == ANET_ERR) {
if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr);
return;
}
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d", cip, cport);
// 处理客户端请求,传入客户端fd,客户端ip
acceptCommonHandler(cfd,0,cip);
}
}
处理客户端请求:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// redis-5.0.3/src/networking.c
static void acceptCommonHandler(int fd, int flags, char *ip) {
client *c;
// 创建 client 对象
// 里面设置fd为 O_NONBLOCK、设置TCP_NODELAY,禁用Nagle算法
// 根据redis.conf配置开关,若开启则设置SO_KEEPALIVE,启用TCP keepalive机制
// 并为该fd注册读事件到epoll,回调函数为 `readQueryFromClient`
if ((c = createClient(fd)) == NULL) {
...
}
...
}
client *createClient(int fd) {
client *c = zmalloc(sizeof(client));
if (fd != -1) {
// 设置套接字为非阻塞
anetNonBlock(NULL,fd);
// 设置 TCP_NODELAY,禁用 Nagle 算法
anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd);
if (server.tcpkeepalive)
anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive);
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE,
readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR)
{
close(fd);
zfree(c);
return NULL;
}
}
...
}
readQueryFromClient负责:
- 解析并查找命令
- 调用命令处理
- 添加写任务到队列
- 将输出写到缓存等待发送
调用链为:readQueryFromClient -> processInputBufferAndReplicate -> processInputBuffer -> processCommand -> call
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// redis-5.0.3/src/server.c
void call(client *c, int flags) {
...
struct redisCommand *real_cmd = c->cmd;
// 调用命令处理函数
c->cmd->proc(c);
}
Redis里redisCommand redisCommandTable[]定义le每个命令对应的处理函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// redis-5.0.3/src/server.c
struct redisCommand redisCommandTable[] = {
{"module",moduleCommand,-2,"as",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"get",getCommand,2,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"set",setCommand,-3,"wm",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"setnx",setnxCommand,3,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"setex",setexCommand,4,"wm",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
...
};
要跟踪命令则找对应处理函数即可,比如get之于getCommand。
整体事件循环流程如下图所示:
3. Nginx中的epoll流程
TODO
4. 小结
梳理Redis中的epoll事件循环,具体逻辑细节暂未展开。Nginx相关epoll使用流程续再梳理。