编译基础知识笔记
整理一些编译基础知识
编译基础知识笔记
1. 引言
近期梳理协程有涉及到编译和汇编相关内容,趁此机会稍微整理编译相关的一些知识和实践笔记,后续增量更新。
部分参考:
说明:本博客作为个人学习实践笔记,可供参考但非系统教程,可能存在错误或遗漏,欢迎指正。若需系统学习,建议参考原链接。
2. 程序编译过程
此处仅说明gcc对C/C++的编译。
gcc对C程序的编译过程:
- 预处理(
preprocessing)- 包含头文件处理、宏定义展开、条件编译处理
- 得到预处理后的代码(
.i文件) gcc -E hello.c -o hello.i
- 编译(
compilation)- 将预处理后的代码转换为汇编代码(
.s文件) - 这是整个编译器最核心的部分,包含:
- 词法分析(Lexical Analysis) →
- 语法分析(Syntactic Analysis) →
- 语义分析(Semantic Analysis) →
- 中间代码生成(Intermediate Code Generation) →
- 优化(Optimization) →
- 目标代码生成(汇编)(Code Generation)
gcc -S hello.i -o hello.s
- 将预处理后的代码转换为汇编代码(
- 汇编(
assembly)- 将汇编代码翻译成机器可识别的目标代码(二进制),生成目标文件(
.o文件)- 对应目标代码生成(机器码),是机器可识别的机器码,而上一步编译中生成的目标代码是汇编语言的目标代码
gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o,或直接gcc -c hello.c -o hello.o
- 将汇编代码翻译成机器可识别的目标代码(二进制),生成目标文件(
- 链接(
linking)- 将多个
.o目标文件和库文件链接在一起,生成可执行文件 gcc hello.o -o hello,或直接gcc hello.c -o hello
- 将多个
3. 汇编
3.1. 基本示例
基于下述简单示例来看下对应的汇编逻辑。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// hello.c
#include <stdio.h>
int sum(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 5;
int s = sum(n1, n2);
printf("n1:%d, n2:%d, sum:%d\n", n1, n2, s);
return 0;
}
3.1.1. gdb查看汇编
gdb ./hello,disassemble命令查看sum和main函数对应的汇编代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
(gdb) disassemble sum
Dump of assembler code for function sum:
0x0000000000401126 <+0>: push %rbp
0x0000000000401127 <+1>: mov %rsp,%rbp
0x000000000040112a <+4>: mov %edi,-0x4(%rbp)
0x000000000040112d <+7>: mov %esi,-0x8(%rbp)
0x0000000000401130 <+10>: mov -0x4(%rbp),%edx
0x0000000000401133 <+13>: mov -0x8(%rbp),%eax
0x0000000000401136 <+16>: add %edx,%eax
0x0000000000401138 <+18>: pop %rbp
0x0000000000401139 <+19>: ret
End of assembler dump.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
(gdb) disassemble main
Dump of assembler code for function main:
0x000000000040113a <+0>: push %rbp
0x000000000040113b <+1>: mov %rsp,%rbp
0x000000000040113e <+4>: sub $0x20,%rsp
0x0000000000401142 <+8>: mov %edi,-0x14(%rbp)
0x0000000000401145 <+11>: mov %rsi,-0x20(%rbp)
0x0000000000401149 <+15>: movl $0xa,-0x4(%rbp)
0x0000000000401150 <+22>: movl $0x5,-0x8(%rbp)
0x0000000000401157 <+29>: mov -0x8(%rbp),%edx
0x000000000040115a <+32>: mov -0x4(%rbp),%eax
0x000000000040115d <+35>: mov %edx,%esi
0x000000000040115f <+37>: mov %eax,%edi
0x0000000000401161 <+39>: call 0x401126 <sum>
0x0000000000401166 <+44>: mov %eax,-0xc(%rbp)
0x0000000000401169 <+47>: mov -0xc(%rbp),%ecx
0x000000000040116c <+50>: mov -0x8(%rbp),%edx
0x000000000040116f <+53>: mov -0x4(%rbp),%eax
0x0000000000401172 <+56>: mov %eax,%esi
0x0000000000401174 <+58>: mov $0x402010,%edi
0x0000000000401179 <+63>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x000000000040117e <+68>: call 0x401030 <printf@plt>
0x0000000000401183 <+73>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x0000000000401188 <+78>: leave
0x0000000000401189 <+79>: ret
End of assembler dump.
3.1.2. Compiler Explorer查看汇编
更友好的方式,通过Compiler Explorer网站上可以直接查看代码和对应的汇编,以不同颜色标记了语句块。如下图所示:
也可见demo链接:compiler explorer demo-link
4. ELF布局
4.1. readelf查看程序启动位置
通过readelf来查看ELF文件对应的头信息,可从 Entry point address 中查看程序启动位置。
以 2fiber 中编译的可执行文件为例操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[root@xdlinux ➜ 2fiber git:(main) ✗ ]$ readelf -h test
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - GNU
ABI Version: 0
Type: EXEC (Executable file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x402230
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 84360 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 14
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 35
Section header string table index: 34
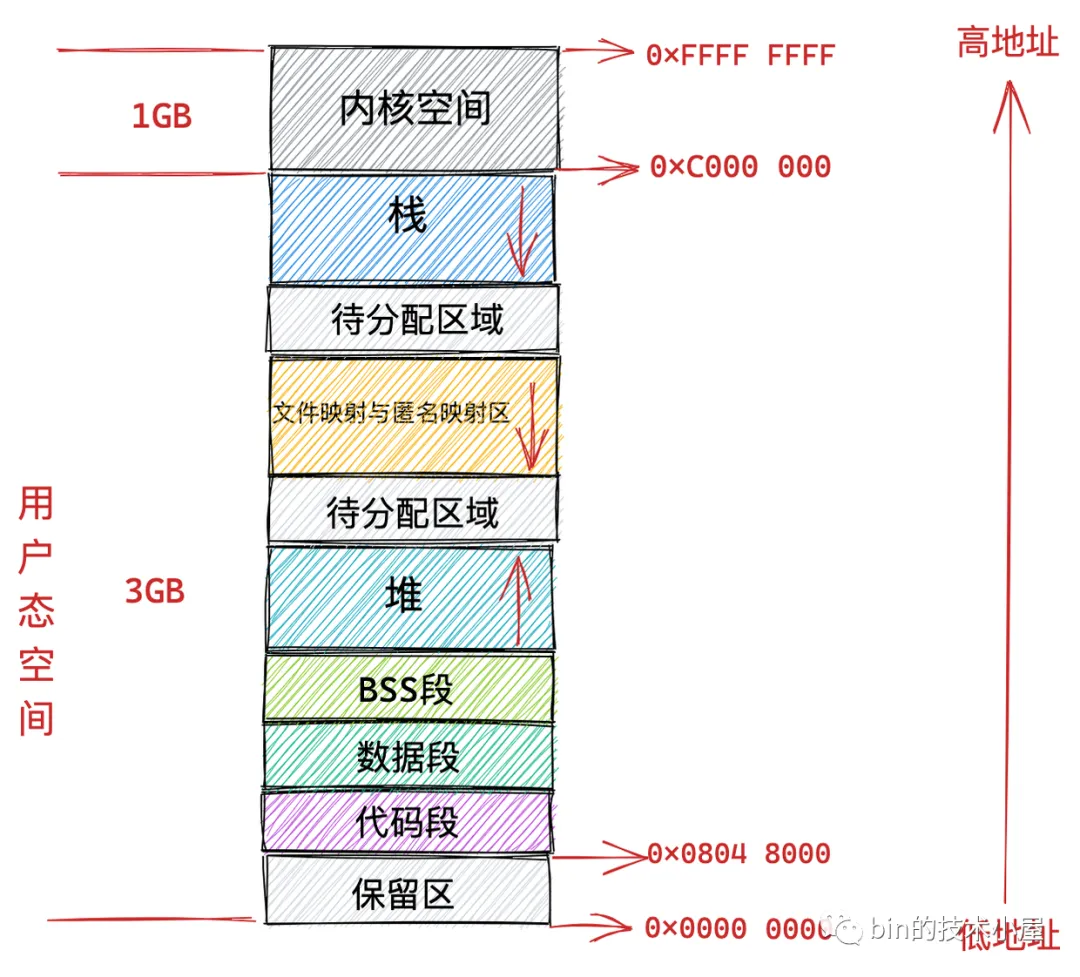
Linux的内存管理和空间分布,可见之前的梳理:CPU及内存调度(二) – Linux内存管理。此处贴一下32位系统下进程的虚拟内存空间分布示意:
4.2. objdump反汇编
objdump对ELF文件进行反汇编:objdump -d test > disassemble_d.txt。
而后查看上述启动地址(0x402230)对应的信息,查找 402230,可看到调用到是__libc_start_main。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# vim disassemble_d.txt
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000402230 <_start>:
402230: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64
402234: 31 ed xor %ebp,%ebp
402236: 49 89 d1 mov %rdx,%r9
402239: 5e pop %rsi
40223a: 48 89 e2 mov %rsp,%rdx
40223d: 48 83 e4 f0 and $0xfffffffffffffff0,%rsp
402241: 50 push %rax
402242: 54 push %rsp
402243: 45 31 c0 xor %r8d,%r8d
402246: 31 c9 xor %ecx,%ecx
402248: 48 c7 c7 d1 3e 40 00 mov $0x403ed1,%rdi
40224f: ff 15 8b 9d 00 00 callq *0x9d8b(%rip) # 40bfe0 <__libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.34>
402255: f4 hlt
402256: 66 2e 0f 1f 84 00 00 nopw %cs:0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
40225d: 00 00 00
5. 全局符号
协程梳理实践(四) – sylar协程API hook封装 中,动态库hook方式小节描述了动态库的全局符号覆盖机制。
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.